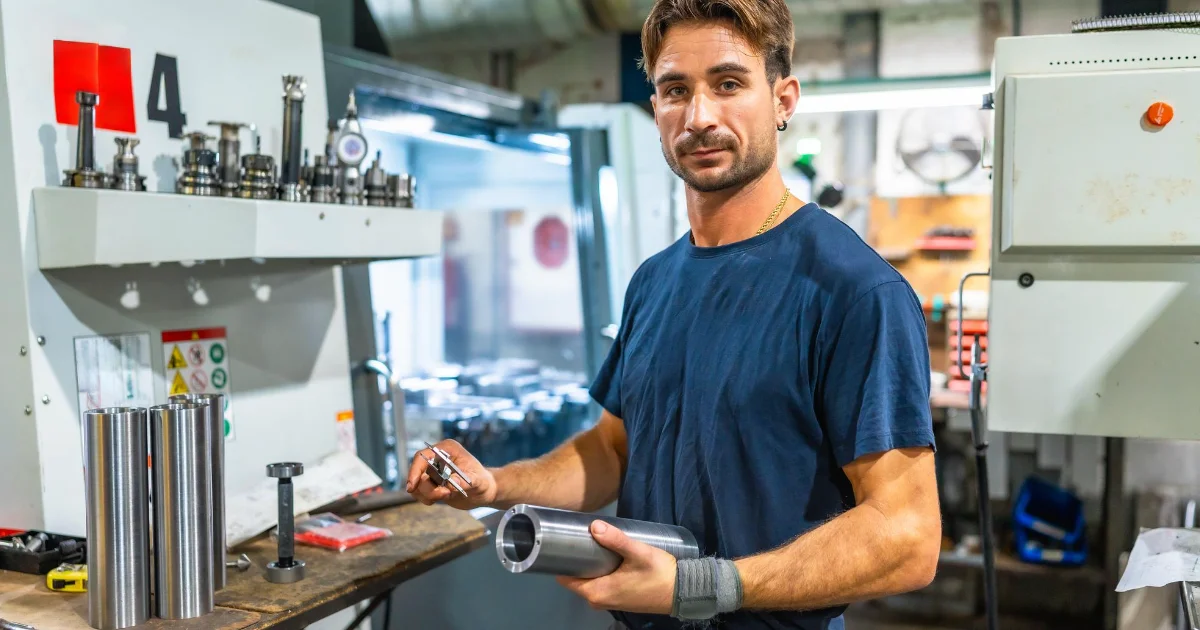
Operator
Operators are expected to be good at:
- Using either control mechanisms or direct physical activity to operate manufacturing systems.
- Working with hand operated industrial machines and power tools.
- Adjusting knobs, levers, and physical or touch sensitive buttons in industrial devices.
- Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or watercraft.
Artisan
Great artisans are usually capable of:
- Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials.
- Performing precise and skillful manipulation of small objects.
- Being active and proactive in regards to physical activities that require considerable use of your arms and legs and moving your whole body, such as climbing, lifting, balancing, walking, stooping, and handling materials.
Other work activities related to Tool and die makers
- Studying blueprints, sketches, models, or specifications for planning sequences of operations for fabricating tools, dies, or assemblies.
- Verifying dimensions, alignments, and clearances of finished parts for conformance to specifications, using measuring instruments such as calipers, gauge blocks, micrometers, or dial indicators.
- Visualize and computing dimensions, sizes, shapes, and tolerances of assemblies, based on specifications.
- Setting up and operating conventional or computer numerically controlled machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, or grinders for cutting, boring, grinding, or otherwise shaping parts to prescribed dimensions and finishes.
- Filing, grinding, shimming, and adjusting different parts for properly fitting them together.
- Placing and assembling parts for making, repairing, or modifying dies, jigs, gauges, and tools, using machine tools and hand tools.
- Conducting testing runs with completed tools or dies for ensuring that parts meet specifications, making adjustments as necessary.
- Inspecting finished dies for smoothness, contour conformity, and defects.