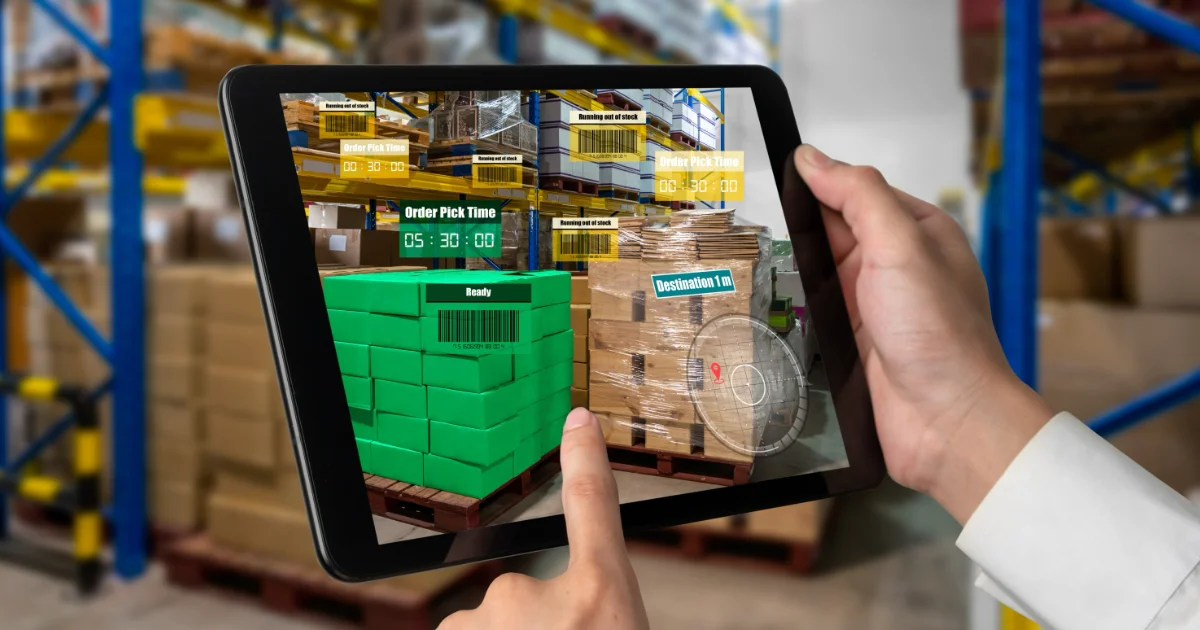
Inspector
Inspectors should be great at:
- Estimating sizes, distances, and quantities; or determining time, costs, resources, or materials needed to perform a work activity.
- Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
- Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
Administrator
Any administrator should excel at:
- Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates, as well as communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail.
- Maintaining information files and processing paperwork.
- Recruiting, interviewing, selecting, hiring, and promoting employees in an organization, and getting them to work together to accomplish tasks by encouraging and building mutual trust, respect, and cooperation.
Other work activities related to Logistics engineers
- Proposing logistics solutions for customers.
- Interviewing key staff or tour facilities for identifying efficiency improvement, cost reduction, or service delivery opportunities.
- Directing the working of logistics analysts.
- Developing specifications for equipment, tools, facility layouts, or material handling systems.
- Reviewing contractual commitments, customer specifications, or related information for determining logistics or assistance requirements.
- Preparing or validate documentation on automated logistics or maintenance data reporting or management information systems.
- Identifying or developing business rules or standard operating procedures to streamline operating processes.
- Developing or maintaining cost estimates, forecasts, or cost models.
- Determining feasibility of designing new facilities or modifying existing facilities, based on factors such as costs, available spaces, schedules, technical requirements, or ergonomics.