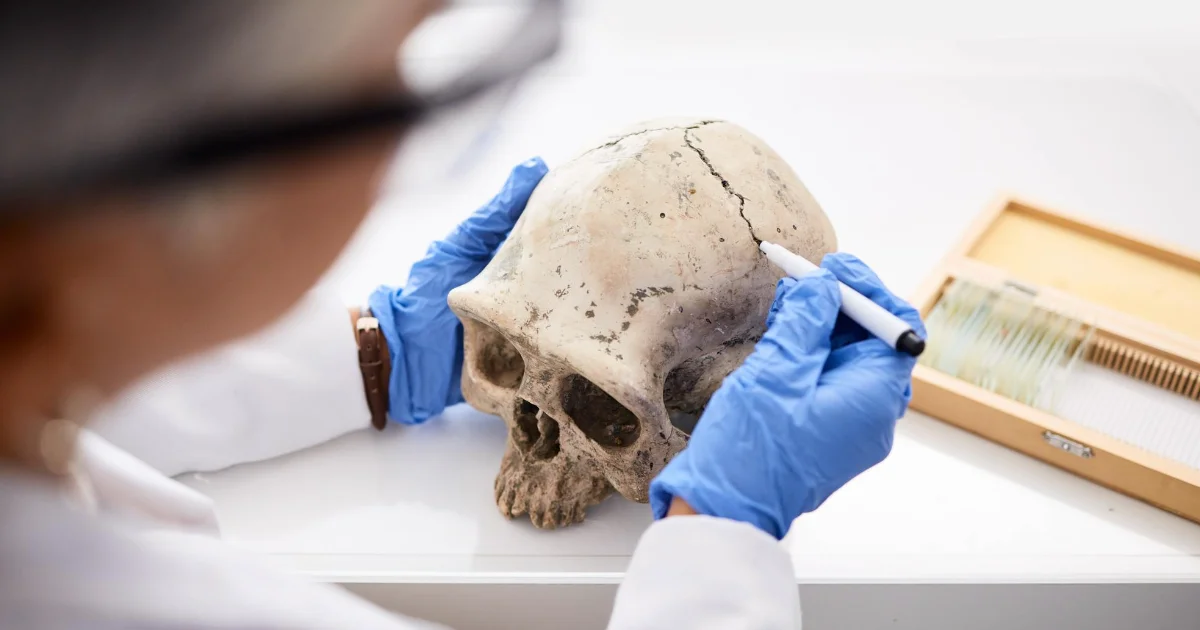
Analyst
Analysts will often perform the following tasks:
- Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts.
- Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
- Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people.
- Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
Inspector
Inspectors should be great at:
- Estimating sizes, distances, and quantities; or determining time, costs, resources, or materials needed to perform a work activity.
- Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
- Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
Other work activities related to Archeologists
- Presenting findings from archeological researching to peers and the general public.
- Writing, presenting, and publish reports for recording site history, methodology, and artifact analysis results, along with recommendations for conserving and interpreting findings.
- Comparing findings from one site with archeological data from other sites for finding similarities or differences.
- Researching, survey, or assessing sites of past societies and cultures searching for answers to specific researching questions.
- Studying objects and structures recovered by excavation for identifying, date, and authenticating them and for interpreting their significance.
- Developing and testing theories concerning the origin and development of past cultures.
- Consulting site reports, existing artifacts, and topographic maps for identifying archeological sites.
- Creating a grid of each site and drawing and updating maps of unit profiles, stratum surfaces, features, and findings.