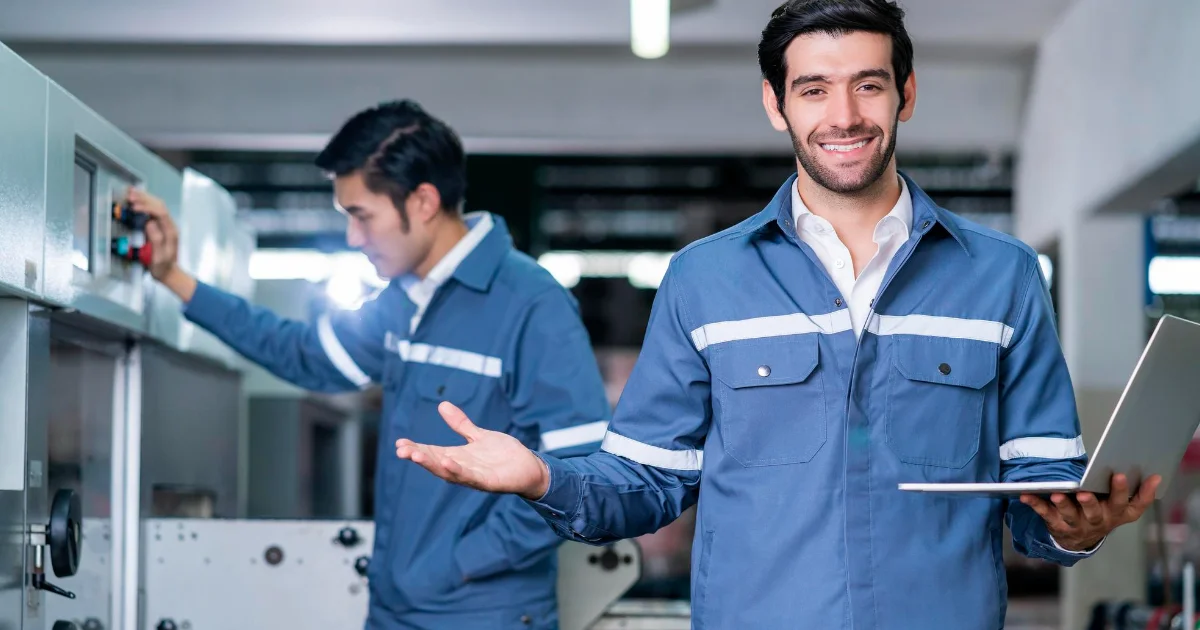
Administrator
Any administrator should excel at:
- Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates, as well as communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail.
- Maintaining information files and processing paperwork.
- Recruiting, interviewing, selecting, hiring, and promoting employees in an organization, and getting them to work together to accomplish tasks by encouraging and building mutual trust, respect, and cooperation.
Mentor
Any mentor is expected to perform well at:
- Identifying the developmental needs of others and coaching, mentoring, or otherwise helping others to improve their knowledge or skills.
- Providing guidance and direction to subordinates, including setting performance standards and monitoring performance.
- Convincing others to accept and idea or to otherwise change their minds or actions in accordance to the companies objectives.
- Identifying the educational needs of others, developing formal educational or training programs or classes, and teaching or instructing others.
Other work activities related to Supervisors of production and operating workers
- Conducting employee training in equipment operations or working and safety procedures, or assigning employee training to experienced workers.
- Keeping records of employees’ attendance and hours worked.
- Directing and coordinating the activities of employees engaged in the production or processing of goods, such as inspectors, machine setters, or fabricators.
- Reading and analyzing charts, working orders, production schedules, and other records and reports for determining production requirements and for evaluating current production estimates and outputs.
- Conferring with other supervisors for coordinating operations and activities within or between departments.
- Planning and establishing working schedules, assignments, and production sequences to meet production goals.
- Inspecting materials, products, or equipment for detecting defects or malfunctions.
- Observing working and monitoring gauges, dials, and other indicators for ensuring that operators conform to production or processing standards.