Technician
Technicians will often be asked these tasks:
- Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
- Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Servicing, repairing, calibrating, regulating, fine-tuning, or testing machines, devices, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of electrical or electronic (not mechanical) principles.
Analyst
Analysts will often perform the following tasks:
- Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts.
- Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
- Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people.
- Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
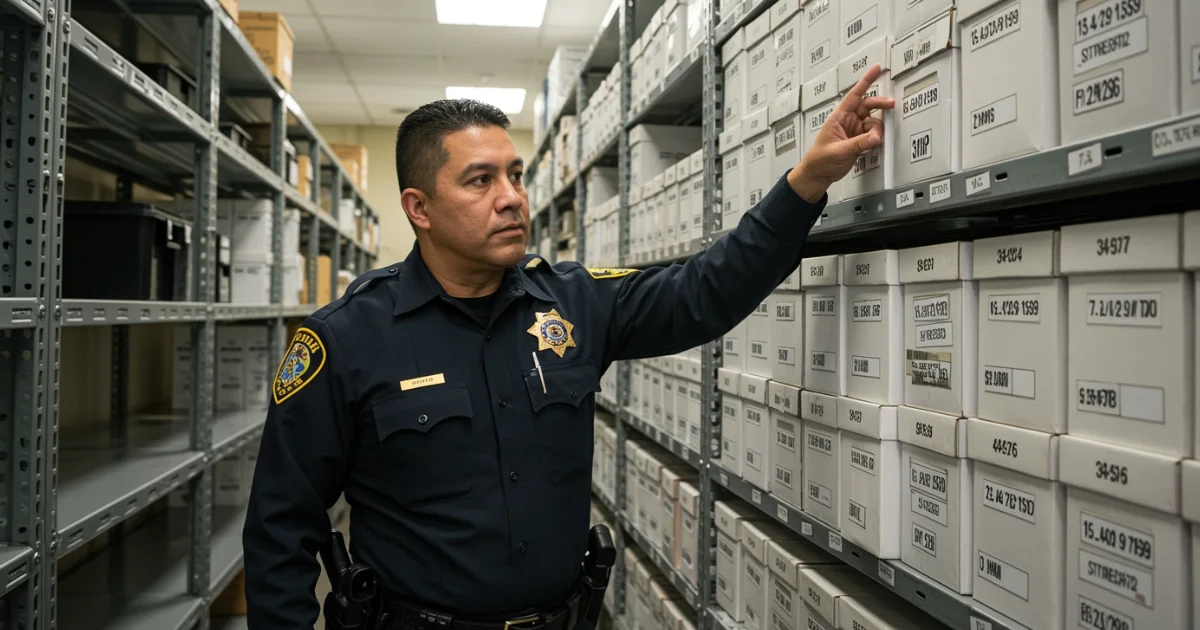
Other work activities related to Police identification and records officers
- Maintaining records of evidence and writing and reviewing reports.
- Submitting evidence to supervisors, crime labs, or court officials for legal proceedings.
- Identifying, comparing, classifying, and file fingerprints, using systems such as Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS) or the Henry Classification System.
- Serving as technical advisor and coordinating with other law enforcement workers or legal personnel for exchanging information on crime scene collection activities.
- Coordinating or conducting instructional classes or in services, such as citizen police academy classes and crime scene training for other officers.
- Interviewing victims, witnesses, suspects, and other law enforcement personnel.
- Analyzing and processing evidence at crime scenes, during autopsies, or in the laboratory, wearing protective equipment and using powders and chemicals.
- Creating sketches and diagrams by hand or with computer software for depicting crime scenes.
- Photographing crime or accident scenes for evidence records.