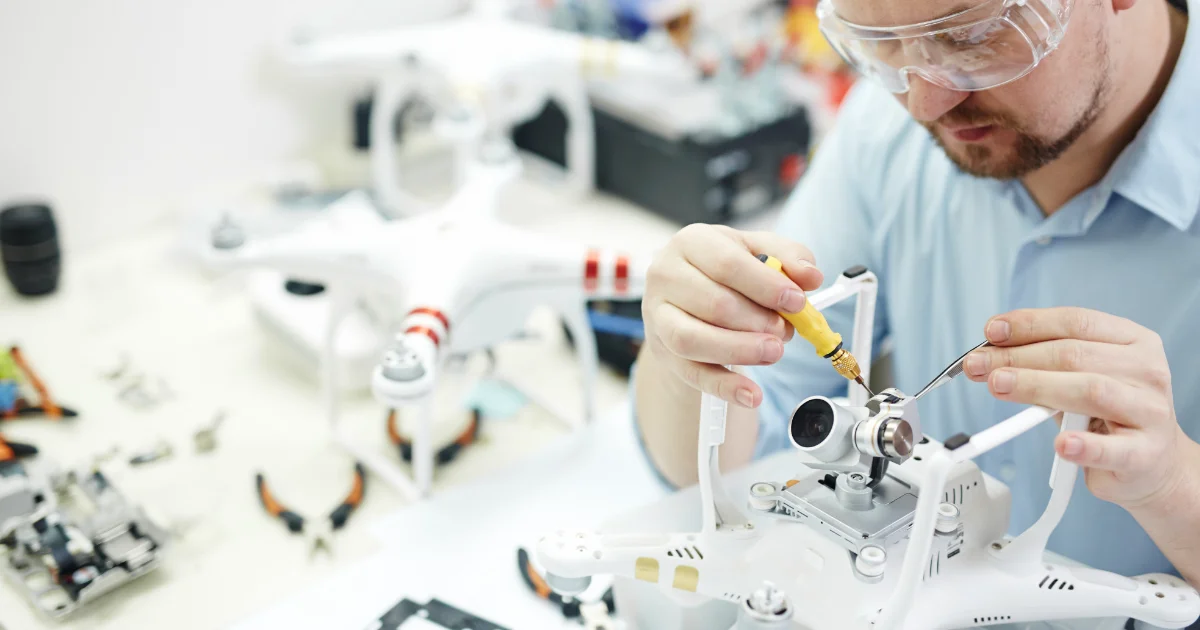
Technician
Technicians will often be asked these tasks:
- Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
- Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Servicing, repairing, calibrating, regulating, fine-tuning, or testing machines, devices, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of electrical or electronic (not mechanical) principles.
Operator
Operators are expected to be good at:
- Using either control mechanisms or direct physical activity to operate manufacturing systems.
- Working with hand operated industrial machines and power tools.
- Adjusting knobs, levers, and physical or touch sensitive buttons in industrial devices.
- Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or watercraft.
Other work activities related to Robotics technicians
- Training customers or other personnel to installing, using, or maintaining robots.
- Programming complex robotic systems, such as vision systems.
- Maintaining service records of robotic equipment or automated production systems.
- Fabricating housings, jigs, fittings, or fixtures, using metalworking machines.
- Documenting robotics testing procedures and results.
- Developing three dimensional simulations of automation systems.
- Inspecting installation sites.
- Modifying computer controlled robot movements.
- Developing robotic path motions for maximizing efficiency, safety, and quality.
- Attaching wires between controllers.
- Assisting engineers in the design, configuration, or application of robotic systems.
- Aligning, fitting, or assembling components, using hand tools, power tools, fixtures, templates, or microscopes.
- Troubleshooting robotic systems, using knowledge of microprocessors, programmable controllers, electronics, circuit analysis, mechanics, sensor or feedback systems, hydraulics, or pneumatics.