Operator
Operators are expected to be good at:
- Using either control mechanisms or direct physical activity to operate manufacturing systems.
- Working with hand operated industrial machines and power tools.
- Adjusting knobs, levers, and physical or touch sensitive buttons in industrial devices.
- Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or watercraft.
Technician
Technicians will often be asked these tasks:
- Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
- Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Servicing, repairing, calibrating, regulating, fine-tuning, or testing machines, devices, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of electrical or electronic (not mechanical) principles.
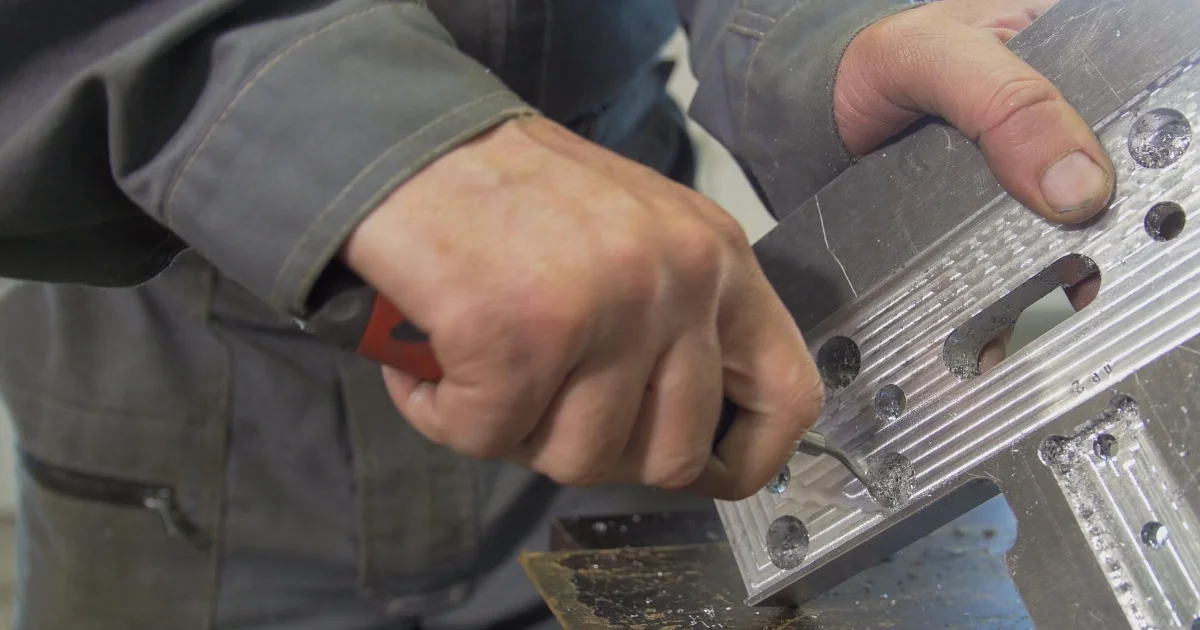
Other work activities related to Model makers, metal and plastic
- Studying blueprints, drawings, and sketches for determining material dimensions, required equipment, and operations sequences.
- Setting up and operating machines, such as lathes, drill presses, punch presses, or bandsaws, for fabricating prototypes or models.
- Inspecting and testing products for verifying conformance to specifications, using precision measuring instruments or circuit testers.
- Cutting, shaping, and forming metal parts, using lathes, power saws, snips, power brakes and shears, files, and mallets.
- Laying out and marking reference points and dimensions on materials, using measuring instruments and drawing or scribing tools.
- Drilling, countersink, and reaming holes in parts and assemblies for bolts, screws, and other fasteners, using power tools.
- Grinding, filing, and sanding parts for finished dimensions.
- Recording specifications, production operations, and final dimensions of models for using in establishing operating standards and procedures.