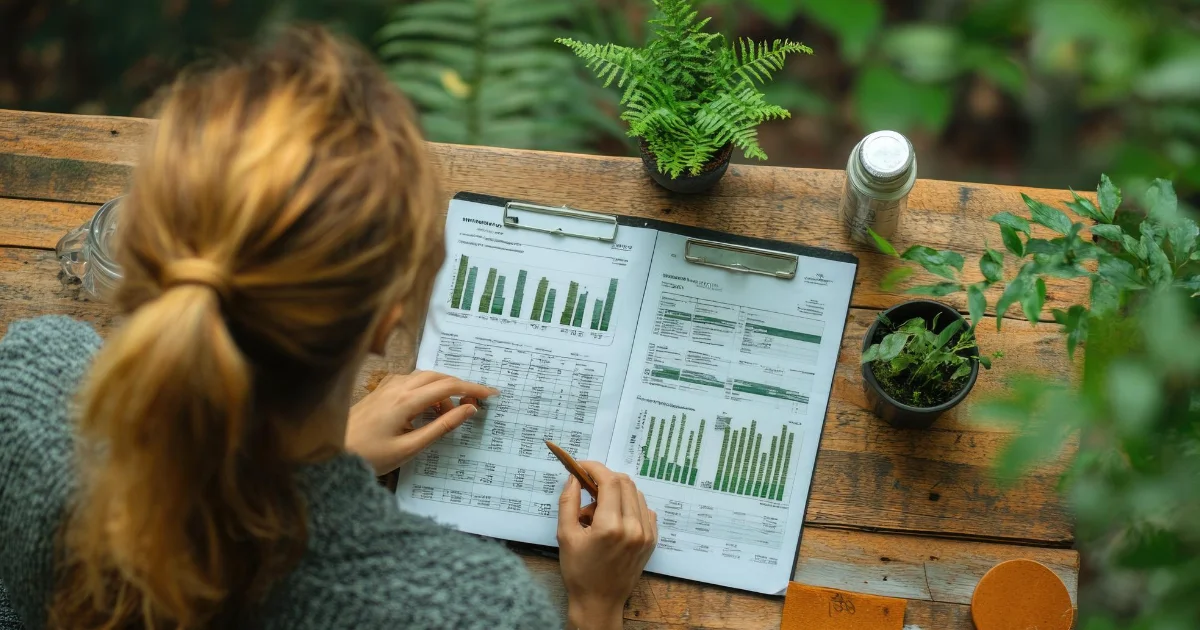
Analyst
Analysts will often perform the following tasks:
- Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts.
- Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
- Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people.
- Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
Technician
Technicians will often be asked these tasks:
- Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
- Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Servicing, repairing, calibrating, regulating, fine-tuning, or testing machines, devices, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of electrical or electronic (not mechanical) principles.
Other work activities related to Biostatisticians
- Teaching graduate or continuing education courses or seminars in biostatistics.
- Reading current literature, attending meetings or conferences, and talk with colleagues for keeping abreast of methodological or conceptual developments in fields such as biostatistics, pharmacology, life sciences, and social sciences.
- Preparing statistical data for inclusion in reports to data monitoring committees, federal regulatory agencies, managers, or clients.
- Preparing articles for publication or presentation at professional conferences.
- Calculating sample size requirements for clinical studies.
- Determining project plans, timelines, or technical objectives for statistical aspects of biological researching studies.
- Assigning working to biostatistical assistants or programmers.
- Writing programming codes for analyzing data using statistical analysis software.
- Writing detailed analysis plans and descriptions of analyses and findings for researching protocols or reports.